Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS)
Carbon Capture, Utilisation, and Storage (CCUS) stands as a transformative technology for industries pursuing decarbonisation. In India, where sectors such as steel, cement, power, fertilisers, and oil and gas drive economic growth, CCUS enables continued industrial development while addressing carbon emissions and climate obligations.
India has committed to net-zero emissions by 2070, supported by a target to capture 750 million metric tonnes of carbon annually by 2050. The Government of India’s ₹39,000 crore investment in carbon capture initiatives highlights the strategic importance of this technology.
Integrated Sustainability Solutions (ISS) by Re Sustainability serves as a trusted partner, delivering tailored CCUS strategies that support national decarbonisation goals and international climate commitments.
Understanding Carbon Capture, Utilisation, and Storage
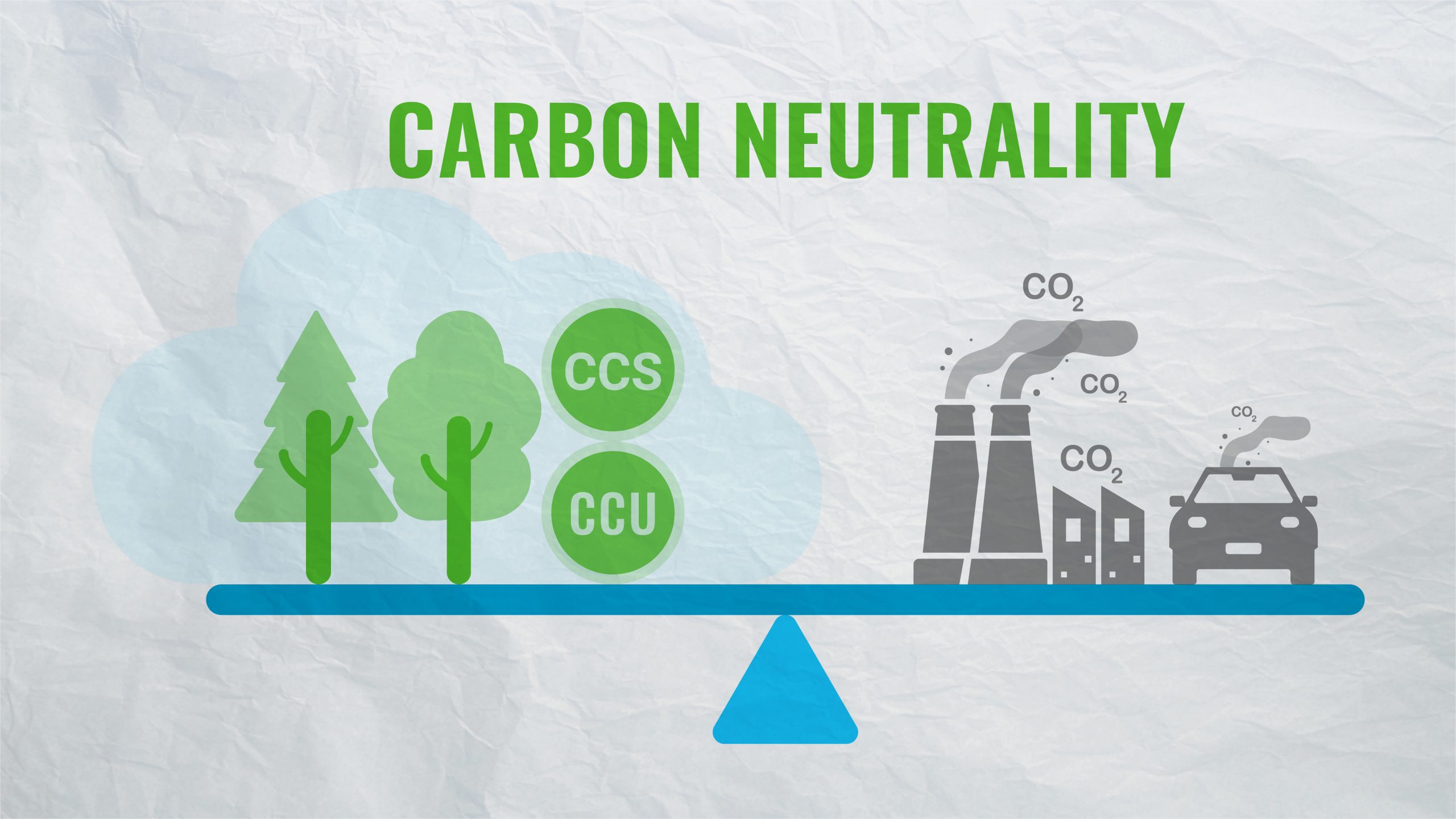
CCUS encompasses technologies that prevent carbon dioxide from entering the atmosphere. Captured carbon is either sequestered permanently in underground geological reservoirs or converted into useful products, including fuels, chemicals, and construction materials.
Key capture methods include:
- Post-combustion capture: Separating carbon dioxide from exhaust gases after fuel
combustion. - Pre-combustion capture: Isolating carbon dioxide from syngas prior to combustion.
- Oxy-fuel combustion: Burning fuel in pure oxygen to produce a carbon dioxide-
concentrated flue stream. - Direct Air Capture (DAC): Extracting carbon dioxide directly from ambient air.
For industries facing limited decarbonisation alternatives, CCUS provides practical, scalable pathways to reduce carbon footprints without compromising operational viability.


India’s Carbon Capture Outlook: From Commitment to Implementation
Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) is globally recognized as essential for achieving climate neutrality. According to the International Energy Agency, over 1.7 billion tons of carbon dioxide must be captured annually by 2030 to remain on a net-zero trajectory.
India is aligning its national strategy with this imperative. The country has pledged net-zero emissions by 2070 and a 45 percent reduction in emissions intensity by 2030. Concrete steps—such as the ₹39,000 crore carbon capture program, incentives for coal-based CCUS projects, and the commissioning of India’s first carbon storage well in Bhopal—signal a decisive transition from policy to action.
Sustainability as a Business Imperative in Oil and Gas
Over the past decade, sustainability has evolved into a core strategic priority for India’s oil and gas sector. Investors, regulators, and local communities now expect verifiable results, not just declarations. The next ten years will separate companies that merely announce change from those that deliver it.
While many industry leaders have established bold decarbonization and ESG targets, the critical challenge lies in execution.

Bridging Ambition with Action
Integrated Sustainability Solutions (ISS) by Re Sustainability provides the operational bridge between vision and reality. Through its specialized brands, ISS enables oil and gas companies to achieve tangible decarbonization outcomes:
- Re Ignite: End-to-end decarbonization strategies and CCUS implementation.
- Re Analytical: Advanced emissions testing, monitoring, and verification.
- NetZero: Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) compliance and carbon credit management.
ISS goes beyond consultancy to deliver full-cycle execution—transforming boardroom commitments into on-site, measurable impact.
- Zero Waste
